Sodium Citrate Tube: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Uses, Colors, and Role in PRP Therapy
Introduction to Sodium Citrate Tube
A sodium citrate tube is a specialized blood collection tube designed for coagulation studies and therapeutic procedures. It contains trisodium citrate, an anticoagulant that prevents blood clotting by binding calcium ions, which are essential for the coagulation cascade. These tubes are widely used in medical diagnostics, PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) therapy, and other anticoagulation treatments.
In this article, we will explore the sodium citrate tube uses, its color coding, composition, and its critical role in PRP test tubes. Whether you’re a medical professional or someone interested in blood collection tubes, this guide will provide valuable insights.
Sodium Citrate Tube Composition and Mechanism
The sodium citrate blood tube contains a liquid or powdered form of trisodium citrate (3.2% or 3.8%), which acts as an anticoagulant. The standard concentration is 3.2% sodium citrate, as it provides optimal coagulation test results.
How Does It Work?
Sodium citrate chelates calcium ions in the blood, preventing clot formation.
This allows plasma to remain liquid for accurate coagulation testing.
The 9:1 blood-to-anticoagulant ratio must be maintained for reliable results.
Sodium Citrate Tube Color Coding
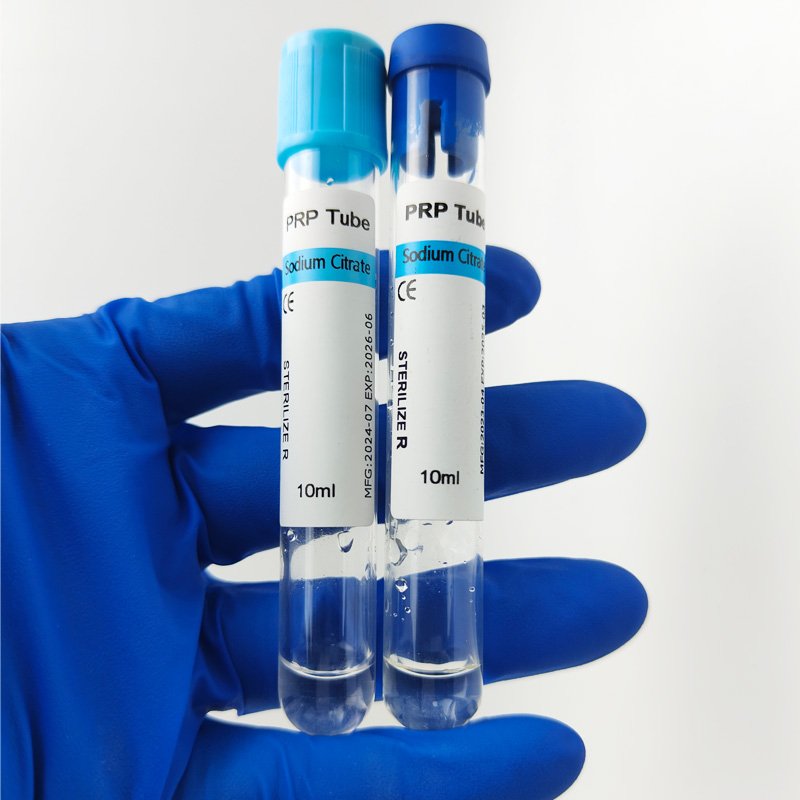
Blood collection tubes follow a universal color-coding system for easy identification. The sodium citrate tube color is typically light blue, distinguishing it from other tubes like EDTA (lavender), heparin (green), or serum tubes (red/gold).
Key Differences in Tube Colors:
| Tube Type | Color | Anticoagulant | Primary Use |
| Sodium Citrate Tube | Light Blue | 3.2% Sodium Citrate | Coagulation tests (PT, aPTT) |
| EDTA Tube | Lavender | EDTA | Hematology (CBC, ESR) |
| Heparin Tube | Green | Lithium/Sodium Heparin | Chemistry tests |
| Serum Separator Tube | Gold/Red | Clot activator + gel | Biochemistry tests |
The plasma separator tube color (often gold or green) differs from the citrate tube, as it contains a gel barrier to separate serum or plasma.
Sodium Citrate Tube Uses in Medical and Aesthetic Fields
The sodium citrate tube uses span across diagnostics and therapeutic applications:
1. Coagulation Testing
Prothrombin Time (PT) and Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT) require citrate tubes for accurate clotting factor analysis.
2. PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) Therapy
PRP test tubes often use sodium citrate to prevent premature clotting while concentrating platelets.
PRP is used in cosmetic treatments (skin rejuvenation, hair restoration) and orthopedic therapies (joint healing).
3. Blood Transfusion & Storage
Citrate tubes help in platelet storage for transfusions.
Sodium Citrate Tube in PRP Therapy
PRP therapy relies on high-quality platelet concentration, and the sodium citrate tube plays a crucial role:
Why Use Sodium Citrate Tubes for PRP?
Prevents Clotting: Ensures platelets remain suspended in plasma.
Maintains Platelet Integrity: Avoids activation before injection.
Improves PRP Yield: Better separation during centrifugation.
PRP Procedure with Sodium Citrate Tubes
Blood Collection: Draw blood into a light blue citrate tube.
Centrifugation: Spin to separate platelets from RBCs.
PRP Extraction: Collect the platelet-rich layer for therapeutic use.
Clinicians prefer sodium citrate PRP tubes over heparin or EDTA tubes because they provide optimal platelet recovery.